Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (40): 6513-6518.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.40.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element modeling and mechanical analysis for Cam-type femoroacetabular impingement
Liu Qian1, Wang Wan-chun1, Yao Chang-hai2
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410011, Hunan Province, China; 2State Key Laboratory of Advanced Design and Manufacture for Vehicle Body, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, Hunan Province, China
-
Revised:2014-08-25Online:2014-09-24Published:2014-09-24 -
Contact:Wang Wan-chun, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410011, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Liu Qian, Studying for doctorate, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410011, Hunan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Qian, Wang Wan-chun, Yao Chang-hai. Finite element modeling and mechanical analysis for Cam-type femoroacetabular impingement[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(40): 6513-6518.
share this article
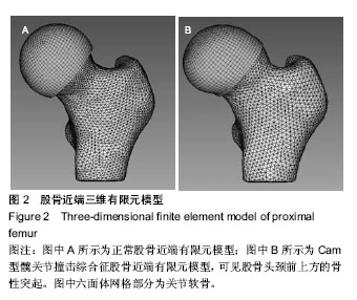
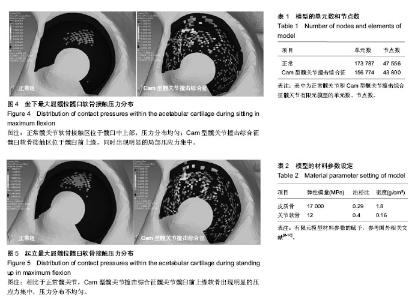
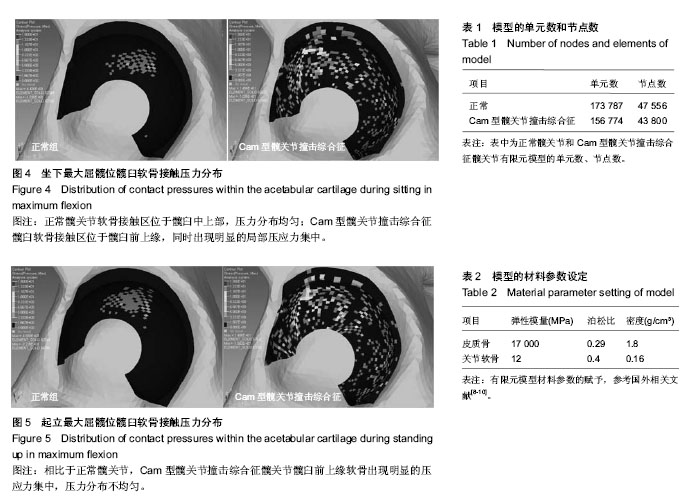
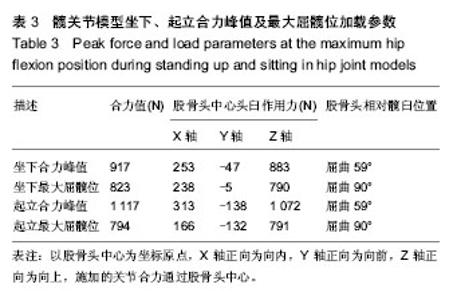
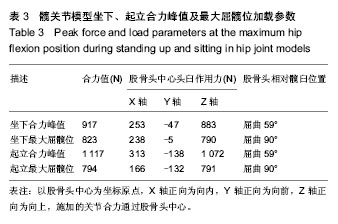
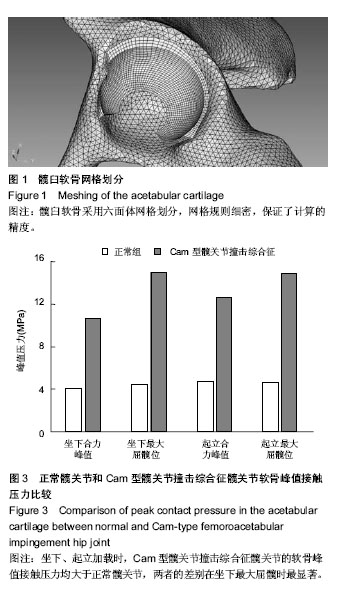
通过有限元计算和分析,得到了髋关节模型在坐下、起立载荷作用下的接触力学特征,包括接触分布形式、接触压力和Von Mises应力。坐下、起立加载时,髋关节软骨接触压力与关节合力大小和屈髋程度相关。正常髋关节在坐下、起立合力峰值时,髋臼软骨峰值接触压力分别为4.11,4.70 MPa,而Cam型FAI髋关节的软骨峰值接触压力为10.62,12.61 MPa. 坐下最大屈髋位加载时,正常髋关节的软骨峰值接触压力为4.43 MPa,Cam型FAI髋关节的软骨峰值接触压力为14.96 MPa;起立最大屈髋位加载时,正常髋关节的软骨峰值接触压力为4.59 MPa,Cam型FAI髋关节为14.86 MPa (图3)。从接触压力分布图可得知,正常髋关节接触区位于髋臼中上部,压力分布均匀;而Cam型FAI髋关节的主要接触区域移至髋臼缘前上方,相比正常髋关节不仅接触位置发生变化,而且出现局部压应力集中(图4,5)。 Von Mises应力即等效应力,Von Mises屈服准则规定,在一定的变形条件下,当受力物体内一点的应力达到某一定值时,该点就开始进入塑性状态。在本文中Von Mises应力反映了软骨内的扭曲力。Cam型FAI髋关节在坐下、起立时,股骨近端的突起部分挤压进入髋臼,引起髋臼前上缘软骨处出现应力集中,峰值Von Mises应力达到12.72 MPa,远大于正常髋关节的4.11 MPa。"
| [1] Ganz R, Parvizi J, Beck M, et al. Femoroacetabular impingement: a cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(417):112-120. [2] Beck M, Kalhor M, Leunig M, et al. Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage: femoroacetabular impingement as a cause of early osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(7): 1012-1018. [3] Harris-Hayes M, Royer NK. Relationship of acetabular dysplasia and femoroacetabular impingement to hip osteoarthritis: a focused review. PMR. 2011;3(11):1055-1067. [4] Notzli HP, Wyss TF, Stoecklin CH, et al. The contour of the femoral head-neck junction as a predictor for the risk of anterior impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(4): 556-560. [5] Pustoc HA, Cheze L. Normal and osteoarthritic hip joint mechanical behaviour: a comparison study. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2009;47(4):375-383. [6] Anderson AE, Ellis BJ, Maas SA, et al. Effects of idealized joint geometry on finite element predictions of cartilage contact stresses in the hip. J Biomech. 2010;43(7): 1351-1357. [7] Anderson AE, Ellis BJ, Maas SA, et al. Validation of finite element predictions of cartilage contact pressure in the human hip joint. J Biomech Eng. 2008;130(5):51008. [8] Dalstra M, Huiskes R, van Erning L. Development and validation of a three-dimensional finite element model of the pelvic bone. J Biomech Eng. 1995;117(3):272-278. [9] Jorge JP, Simoes FM, Pires EB, et al. Finite element simulations of a hip joint with femoroacetabular impingement. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2012. [10] Shepherd DE, Seedhom BB. A technique for measuring the compressive modulus of articular cartilage under physiological loading rates with preliminary results. Proc Inst Mech Eng H.1997;211(2):155-165. [11] Caligaris M, Ateshian GA. Effects of sustained interstitial fluid pressurization under migrating contact area, and boundary lubrication by synovial fluid, on cartilage friction. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16(10):1220-1227. [12] Bergmann G, Deuretzbacher G, Heller M, et al. Hip contact forces and gait patterns from routine activities. J Biomech. 2001;34(7):859-871. [13] Adams D, Swanson SA. Direct measurement of local pressures in the cadaveric human hip joint during simulated level walking. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985;44(10):658-666. [14] Brown TD, Shaw DT. In vitro contact stress distributions in the natural human hip. J Biomech. 1983;16(6):373-384. [15] Rushfeldt PD, Mann RW, Harris WH. Improved techniques for measuring in vitro the geometry and pressure distribution in the human acetabulum. II Instrumented endoprosthesis measurement of articular surface pressure distribution. J Biomech. 1981;14(5):315-323. [16] Carlson CE, Mann RW, Harris WH. A radio telemetry device for monitoring cartilage surface pressures in the human hip. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1974;21(4):257-264. [17] Hodge WA, Fijan RS, Carlson KL, et al. Contact pressures in the human hip joint measured in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986;83(9):2879-2883. [18] Afoke NY, Byers PD, Hutton WC. Contact pressures in the human hip joint. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987;69(4):536-541. [19] Sparks DR, Beason DP, Etheridge BS, et al. Contact pressures in the flexed hip joint during lateral trochanteric loading. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(2):359-366. [20] von Eisenhart R, Adam C, Steinlechner M, et al. Quantitative determination of joint incongruity and pressure distribution during simulated gait and cartilage thickness in the human hip joint. J Orthop Res. 1999;17(4):532-539. [21] Wagner S, Hofstetter W, Chiquet M, et al. Early osteoarthritic changes of human femoral head cartilage subsequent to femoro-acetabular impingement. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2003;11(7):508-518. [22] Bittersohl B, Hosalkar HS, Kim YJ, et al. Delayed gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (dGEMRIC) of hip joint cartilage in femoroacetabular impingement (FAI): Are pre- and postcontrast imaging both necessary? Magn Reson Med. 2009;62(6):1362-1367. [23] Bittersohl B, Steppacher S, Haamberg T, et al. Cartilage damage in femoroacetabular impingement (FAI): preliminary results on comparison of standard diagnostic vs delayed gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of cartilage (dGEMRIC). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(10): 1297-1306. [24] Jessel RH, Zilkens C, Tiderius C, et al. Assessment of osteoarthritis in hips with femoroacetabular impingement using delayed gadolinium enhanced MRI of cartilage. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;30(5):1110-1115. [25] Sah RL, Kim YJ, Doong JY, et al. Biosynthetic response of cartilage explants to dynamic compression. J Orthop Res. 1989;7(5):619-636. [26] Harris MD, Reese SP, Peters CL, et al. Three-dimensional quantification of femoral head shape in controls and patients with cam-type femoroacetabular impingement. Ann Biomed Eng. 2013;41(6):1162-1171. [27] Chegini S, Beck M, Ferguson SJ. The effects of impingement and dysplasia on stress distributions in the hip joint during sitting and walking: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(2):195-201. [28] Buschmann MD, Kim YJ, Wong M, et al. Stimulation of aggrecan synthesis in cartilage explants by cyclic loading is localized to regions of high interstitial fluid flow. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999;366(1):1-7. [29] Kim YJ, Sah RL, Grodzinsky AJ, et al. Mechanical regulation of cartilage biosynthetic behavior: physical stimuli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994;311(1):1-12. [30] Parkkinen JJ, Lammi MJ, Helminen HJ, et al. Local stimulation of proteoglycan synthesis in articular cartilage explants by dynamic compression in vitro. J Orthop Res. 1992;10(5):610-620. [31] Kurz B, Jin M, Patwari P, et al. Biosynthetic response and mechanical properties of articular cartilage after injurious compression. J Orthop Res. 2001;19(6):1140-1146. [32] Piscoya JL, Fermor B, Kraus VB, et al. The influence of mechanical compression on the induction of osteoarthritis- related biomarkers in articular cartilage explants. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(12):1092-1099. [33] Torzilli PA, Grigiene R, Huang C, et al. Characterization of cartilage metabolic response to static and dynamic stress using a mechanical explant test system. J Biomech. 1997; 30(1):1-9. [34] O'Hara BP, Urban JP, Maroudas A. Influence of cyclic loading on the nutrition of articular cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990; 49(7):536-539. [35] Beaule PE, Zaragoza E, Motamedi K, et al. Three-dimensional computed tomography of the hip in the assessment of femoroacetabular impingement. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(6):1286-1292. [36] Konrath GA, Hamel AJ, Olson SA, et al. The role of the acetabular labrum and the transverse acetabular ligament in load transmission in the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998; 80(12):1781-1788. [37] Ateshian GA, Ellis BJ, Weiss JA. Equivalence between short-time biphasic and incompressible elastic material responses. J Biomech Eng. 2007;129(3):405-412. |
| [1] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [2] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [3] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [4] | Li Peng, Li Hong-wei, Wang Shuang, Wang Hai-zhou. Digital anatomy of lumbar spinous process tilt angle of adults in northeast China: prodinding reference for pedicle screw insertion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1064-1068. |
| [5] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [6] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [7] | Qin Di, Shang Yong-wei, Li Hui-jie, Han Yong-tai. Collapsed femoral head measured by X-ray and CT before hip replacement: study protocol for a single-center, open-label and diagnostic trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1080-1085. |
| [8] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [9] | Yao Yu, Xue Hua-wei, Zhao Jian, Zhang Feng, Cao Yong, Chen Xiang-dong, Zhao Jin-long, Jiang Xing-jie. Biomechanics of lumbar cortical bone trajectory screw fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 362-366. |
| [10] | Chen Lu-yao, Hu Shi-qiang, Wang Xiao-ping, Wu Wei-wei, Wei Zhan-tu, Huang Jian. Accuracy of digital orthopedic three-dimensional reconstruction for thoracolumbar pedicle screw placement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 373-377. |
| [11] | Du Shi-yao, Zhou Feng-jin, Ni Bin, Chen Bo, Chen Jin-shui. Finite-element analysis of a novel posterior atlantoaxial restricted non-fusion fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 383-389. |
| [12] | Liu Jun, Liao Su-ping. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of Kirschner nails and external fixation for Bennett fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 390-395. |
| [13] | Zhang Li-chao, Zhang Li-min, Lv Yong-ming, Wang Zhi-hui, Yang Yang, Xu Fei, Dai Hai-feng, Li Jia, Cao Xiang-yu, Wu Li-zhu. Finite element analysis of knee flexion and extension movement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 396-400. |
| [14] | Jia Jin-ling, Dong Yu-zhen. Finite element analysis of prosthesis position during hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 401-405. |
| [15] | Wang Xiu-ping, Sun Rui-bo, Liu You-wen, Zhang Ying, Jia Yu-dong, Yang Yu-xia, Wang Hui-chao. Femoral neck fractures fixed with intramedullary cannulated screws: factors for postoperative functional recovery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 2999-3004. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||